Birds have long enthralled the imagination of man and his varied abilities, from flying high up in the skies to gliding down to placidly float on the surface of water. Amongst these marvelous birds is a special category that is termed “fortunate swimming birds.” These birds are blessed with unique adaptations that help them to swim effortlessly through the aquatic environment. But what exactly is a fortunate swimming bird and why are they termed “fortunate”? Let’s dive deep into this fascinating topic.
Understanding the Term “Fortunate Swimming Bird”

The term “fortunate swimming bird” refers to birds that are exceptionally well-adapted to swimming, thriving, and living in aquatic environments. Their “fortune” lies in their evolutionary traits that equip them well enough to swim, dive, and forage effectively in water. Such birds have realized advantages through special physical features, such as webbed feet, waterproof feathers, and streamlined bodies, which improve their swimming abilities and enable food exploitation from lakes, rivers, oceans, and wetlands.
Characteristics of Fortunate Swimming Birds
Fortunate swimming birds have their own unique features apart from the land-dwelling or aerial counterparts. Some of the primary traits that define these remarkable birds are listed as follows:
- Webbed Feet: One of the defining features of swimming birds is the webbed feet. These function like paddles and enable them to propel themselves through water with very little effort. The webbing between their toes increases the surface area of each stroke, making it more powerful and efficient.
- Waterproof Feathers: Swimming birds often have waterproof feathers coated with natural oils. That helps prevent waterlogging of feathers, making them remain buoyant and dry even if they stay immersed in water for a long period.
- Streamlined Bodies: Reduced drag in water from a streamlined body shape allows these birds to swim without much problem. The same design is also hydrodynamically useful for diving and chasing prey underwater.
- Strong Muscles: Fortunate swimming birds are powerful in the muscles of their legs and wings, enabling them to paddle with high efficiency or swim using only their wings and an underwater propulsion.
- Specialized Beaks: Many swimming birds are adapted to specific diets through beak specialization. Ducks, for example have flat, sieve-like bills which facilitate the filtration of food particles in water, and cormorants have hooked beaks, perfectly suited to capture fish.
Examples of Fortunate Swimming Birds
Several bird species are fortunate swimming birds. Let’s look at a few of the most prominent examples:
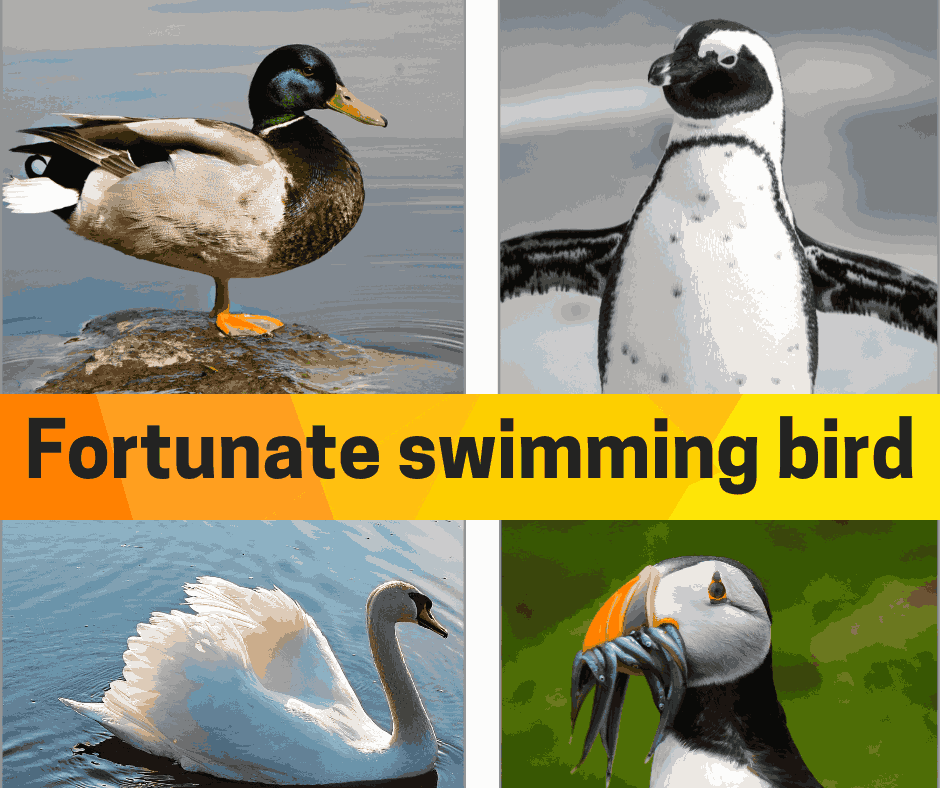
- Ducks: Ducks are perhaps the most iconic swimming birds. They swim effortlessly in both freshwater and saltwater habitats across the globe with their webbed feet and buoyant bodies. Ducks are opportunistic feeders, eating everything from aquatic plants to small fish.
- Penguins: Penguins are flying birds with impressive swimming abilities. Hailing from the Southern Hemisphere, these birds swim using their flippers as if they were wings in water. Penguins are a very specialized animal adapted to the marine environment, diving to deep levels in the hunt for fish and krill.
- Swans: Swans are large, well-built aquatic birds found in most freshwater habitats. Large necks and strong legs can submerge them in water for effective feeding while their grace has made it a symbol of beauty and elegance.
- Cormorants: Cormorants are diving experts and superb swimmers. These birds have less oily feathers, which means that they become less buoyant for underwater hunting. Cormorants are often seen drying their wings in the sun when they have finished swimming.
- Puffins: Puffins are little seabirds with colorful beaks, but exceptional swimming skills. They use their wings to propel themselves underwater and are good at catching fish.
Why Are These Birds Considered “Fortunate”?
The term “fortunate” in “fortunate swimming bird” shows the evolutionary advantages these birds have. Here are some reasons why they are deemed fortunate:
- Availability of Lush Food Sources: Aquatic ecosystems are full of food, such as fish, crustaceans, aquatic plants, and algae. Swimming birds lucky enough to find these can feed on them, thus becoming better off compared to other animals.
- Robustness of Environmental Adaptation: Swimming birds live in diverse habitats, from oceans to rivers, lakes, and wetlands. The birds can be able to sustain themselves in fluctuating environmental factors.
- Natural Protection Features: Swimming birds can easily evade predators because they can dive underwater, which is a capability that many land-dwelling birds lack. Their speed and agility in water make them less vulnerable to threats.
- Ecological Significance: Lucky swimming birds are crucial to their ecosystems. They feed on aquatic organisms, which helps to maintain the balance of food webs in aquatic environments.
Challenges Faced by Fortunate Swimming Birds
Although these birds are blessed with the best evolutionary advantages, there are many problems that they face in the present world:
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization, deforestation, and pollution have destroyed aquatic habitats, making many swimming bird species endangered.
- Climate Change: Increased temperatures and changes in weather patterns alter ecosystems, thereby affecting the food supply and breeding grounds of swimming birds.
- Pollution: Oil spills, plastic waste, and water pollution are all threats to aquatic birds. They can die from ingesting plastics or getting entangled in debris.
- Overfishing: Overfishing decreases the availability of prey for piscivorous birds, which then have to compete for scarce resources.
Conservation Efforts
- Wetland, River, and Coastal Area Restoration: The wetlands, rivers, and coastal areas are restored for swimming birds, which gives them a safe breeding and feeding ground.
- Pollution Control: Plastic waste is reduced, oil spills are cleaned up, and water pollution is minimized to ensure the safety of aquatic birds.
- Legal Protection: Many countries have enacted laws that protect the species of swimming birds and their habitats. International treaties, such as the Migratory Bird Treaty Act, also help.
- Public Awareness Activities: Public awareness of the necessity of aquatic birds as well as their environment will encourage conservation efforts.
Fun Facts About Fortunate Swimming Birds
- Penguins are able to swim at a rate of 15 mph.
- Ducks possess three eyelids to protect their eyes when swimming.
- Some puffins have tongues able to hold several fish in their mouths.
- Cormorants dive to depths of 150 feet while hunting for fish.
Conclusion
Fortunate swimming birds are indeed marvelous creatures that demonstrate the wonders of evolution and adaptation. Their unique features allow them to thrive in aquatic environments, making them vital contributors to the health and balance of ecosystems. However, these birds face significant threats, and it is our responsibility to ensure their survival through conservation efforts and sustainable practices. If we admire and protect these “lucky” swimmers, we ensure that not only is their beauty preserved but also the balance of our planet’s ecosystem.